|
A
System for Limb-Volume Measurement using 3D Models from an
Infrared Depth Sensor
by
Guannan Lu
Introduction
Lymphedema, a chronic disease
caused by failure in the lymphatic system, affects nearly
500,000 people in the U.S., and over 2.4 million breast cancer
survivors are at-risk for developing this disease at some point
in their life. Early detection and management can significantly
reduce the potential for symptoms and complications; however,
many patients fail to seek medical assistance at the first sign
of the disease. In this project, we present a method for
measuring limb volume and for detecting early swelling
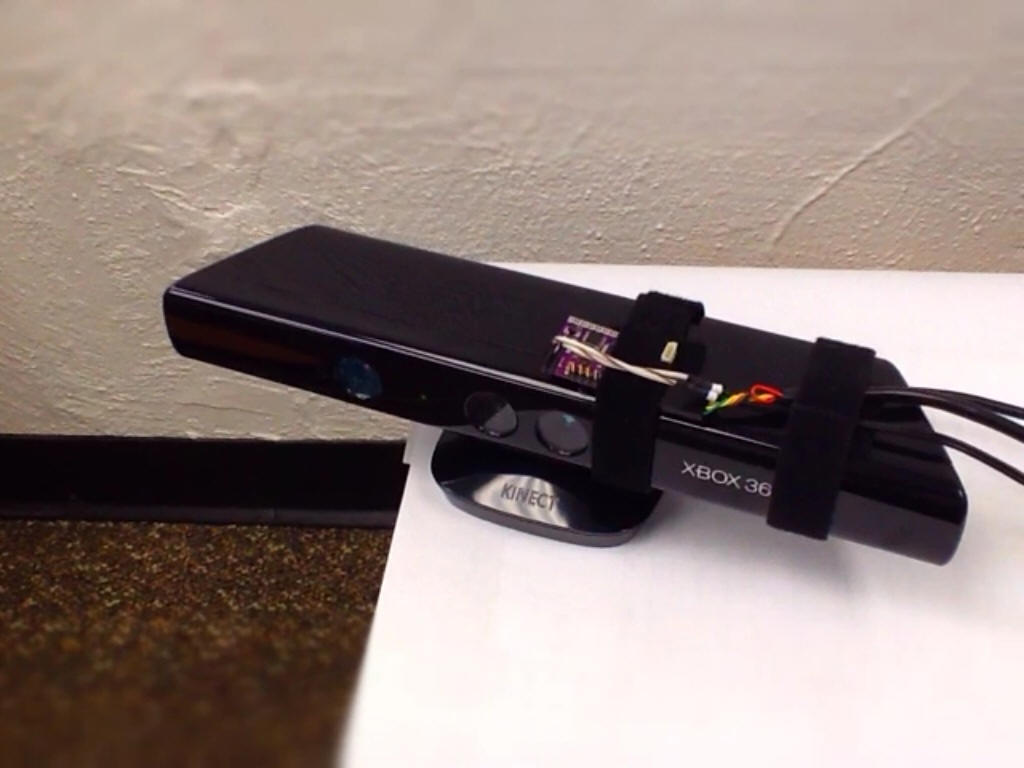
associated with lymphedema. The system relies on IR imaging
sensors, such as in the Microsoft Kinect. This technique will
allow for the future development of tools for self-management
and specialist monitoring, and when compared to other
commercially available devices, our system is less expensive,
equally or more reliable/accurate, and much more user friendly.
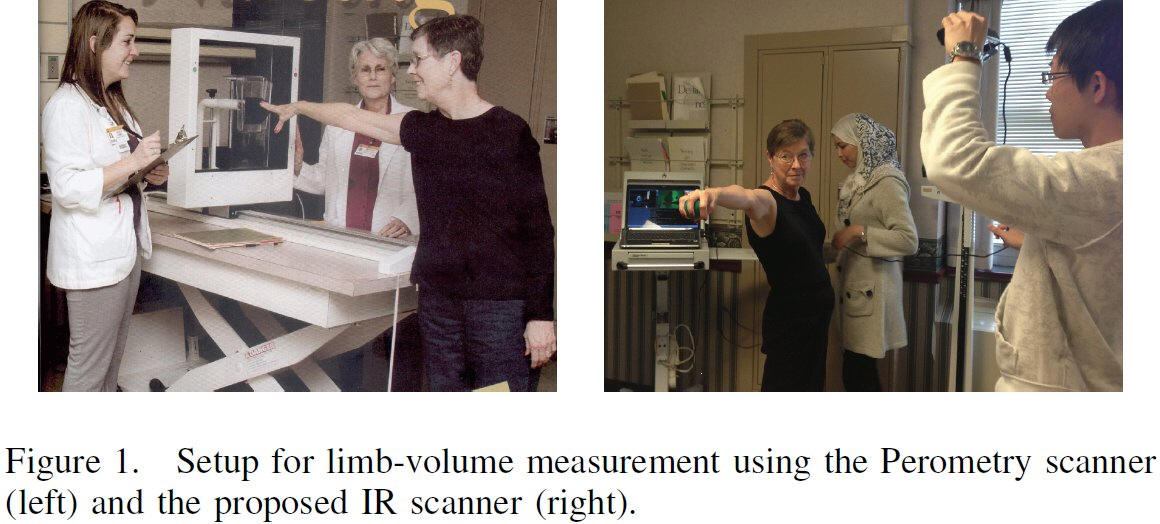
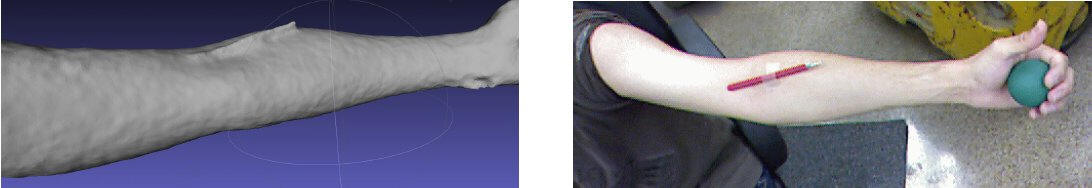
Our Technique versus Water Displacement
The proposed technique for limb-volume measurement
was compared with the water displacement and the perometry. In
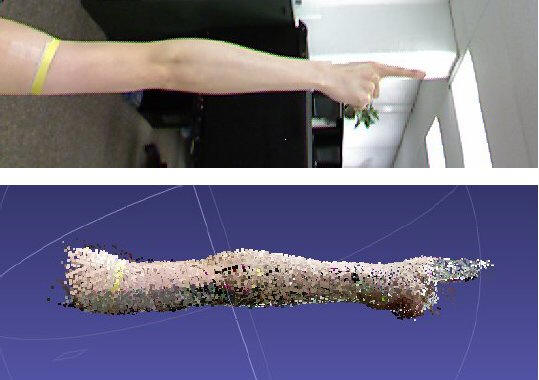
this project, a series of improvements made to the system is
presented. The changes led to the complete automation of the
process of 3D imaging the arms. Being an
ongoing research, the results presented here are limited to 14
arms of healthy volunteers. In the future, test will include a
larger number of limbs of healthy as well as cancer patients.

Same technology can be used for can be used for Dermatology
Virtual Dermatologist
Under
Construction... by
Dao Lam
by
Dao Lam
|
|
3D Model created using Virtual Cameras
(click on the image to play the video) |
References
-
G. Lu, G. N. DeSouza, J. Armer, B. Anderson, and C.-R. Shyu,
Comparing Limb-Volume Measurement Techniques: 3D Models from
an Infrared Depth Sensor versus Water Displacement, in
2013 International Conference on e-Health Networking,
Applications and Services. (Submitted)
-
G. Lu, G. N. DeSouza, J. Armer, B. Anderson, and C.-R. Shyu,
A
system for limb-volume measurement using 3d models from an
infrared depth sensor, in 2013 IEEE Symposium Series on
Computational Intelligence, Symposium on Computational
Intelligence for Healthcare and e-Health (CICARE), Apr 2013,
pp. 6469, singapore.
-
D. Lam and
G. N. DeSouza , Virtual dermatologist: An application of 3D
modeling to tele-healthcare, in Proceedings of the 13th
IEEE International Conference on e-Health Networking,
Application & Services, June 2011, pp. 2833, colubmia, MO
(Selected for Best Paper Award).
See this paper on IEEE.org
-
D. Lam, R.
Hong, and G. N. DeSouza , 3D human modeling using virtual
multi-view stereopsis and motion estimation, in Proceedings
of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent
Robots and Systems, Oct. 2009, pp. 42944299.
See this paper on IEEE.org
-
J. Park
and G. N. DeSouza, 3-D Modeling of Real-World Objects Using
Range and Intensity Images., ser. Studies in Computational
Intelligence, B. Apolloni, A. Ghosh, F. N. Alpaslan, L. C.
Jain, and S. Patnaik, Eds. Springer-Verlag, 2005, vol. 7.
[Online]. Available:
http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/series/sci/sci7.html#ParkD05
|