|
Image-based Visual Servoing
by Yuanqiang Evan
Dong
Introduction
Any control system using
visual-sensory feedback loops falls into one of four categories. These
categories are derived from choices made regarding two criteria: the coordinate
space of the error function, and the hierarchical structure of the control
system. These choices will determine whether the system is a position-based
or an image-based system, as well as if it is a dynamic look-and-move
or a direct visual servo.
In our work, we present an
image-based, dynamic look and move visual servoing system. The
difference between our approach and other popular ones is in the use of
quaternion representation, which eliminates the potential singularities
introduced by a rotational matrix representation.
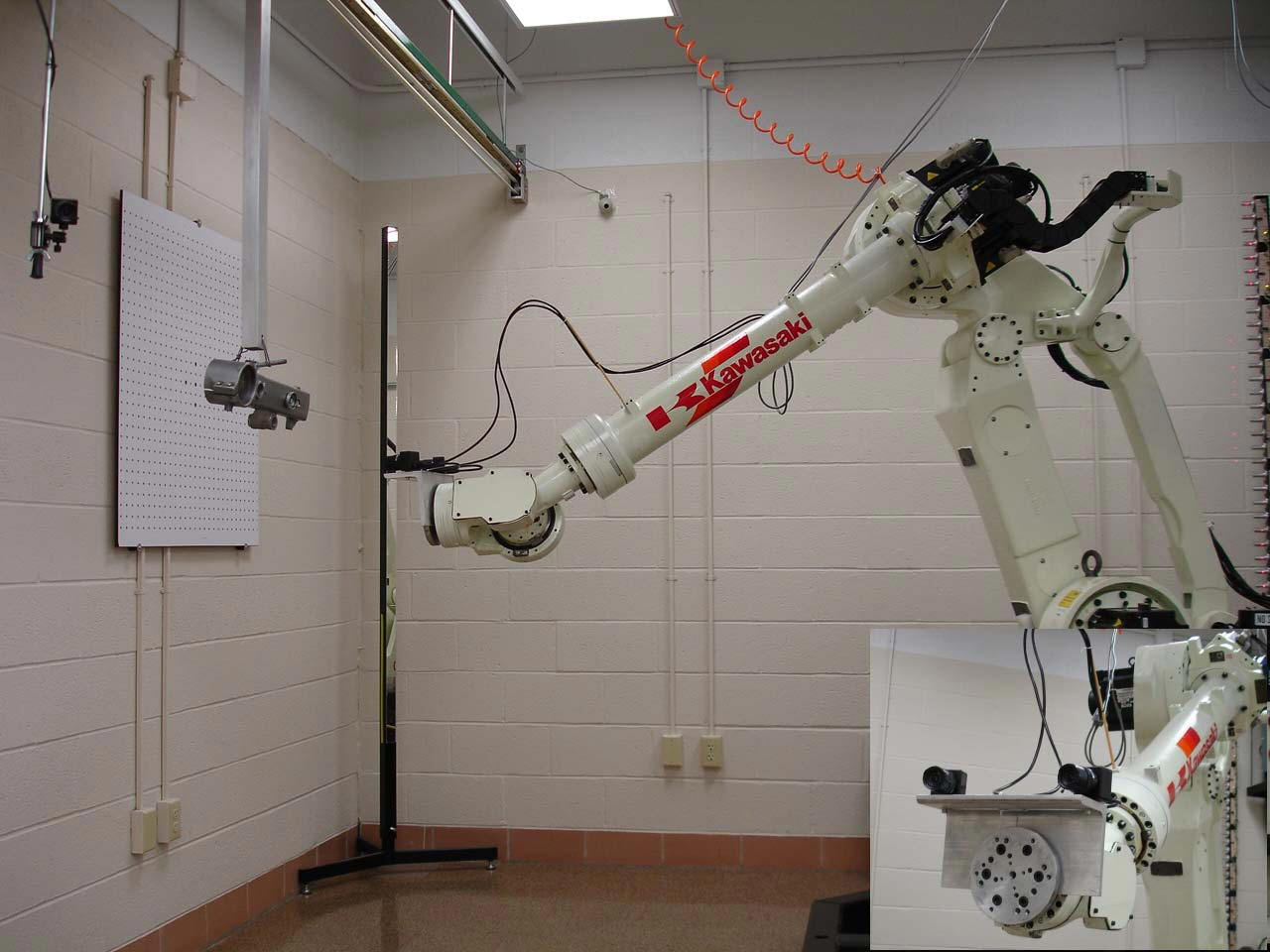
Results
This visual servoing system was
tested in real Kawasaki robot. Specifically, the system was tested in three
different scenarios: pure linear motion, pure angular motion and hybrid motion.
A.
Pure linear motion
B.
Pure angular motion
C.
Hybrid motion
References
-
Koenig, T., Dong, Y., and DeSouza, G. N., "Image-based Visual
Servoing of a Real Robot Using a Quaternion Formulation," in the Proceedings
of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation & Mechatronics (RAM), pp.
216-221 Sept./08, China.
-
Koenig, T., and DeSouza, G. N., "Implementation of a Homography-based
Visual Servo Control using a Quaternion Formulation," in the Proceedings of
the 2008 IFAC International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and
Robotics (ICINCO), pp. 288-294, May 2008, Portugal
-
DeSouza G.N. and Kak A.C.,
"
A Subsumptive, Hierarchical, and Distributed Vision-Based
Architecture for Smart Robotics",
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Part B,
Vol. 34, No. 5, Oct. 2004.
|