|
Path Planning in Dynamic
Environments Using Time Warps
by
Siavash Farzan
Introduction
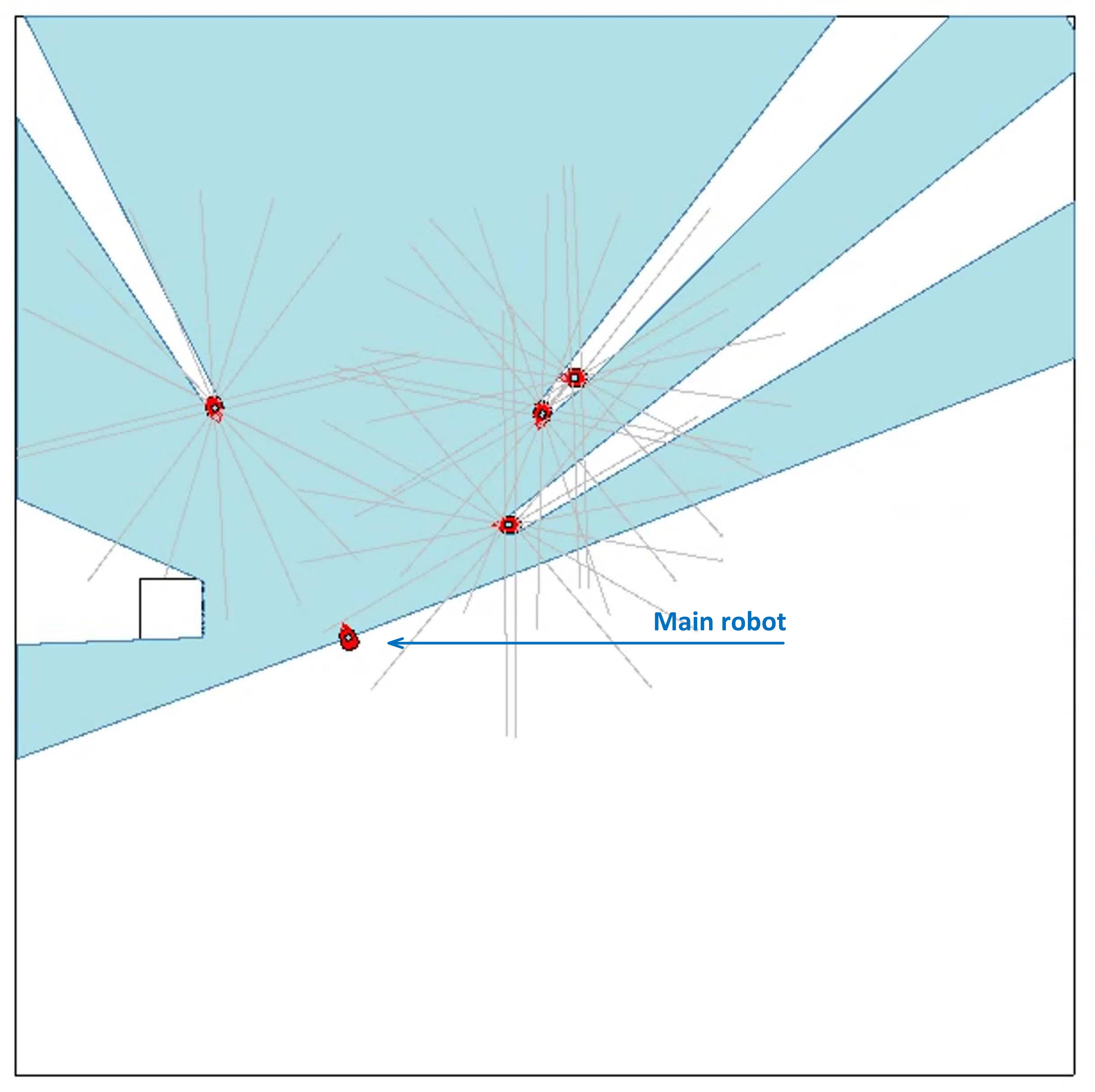
The objective of path planning is to find a suitable path
between two specific positions in an environment, which does not
collide with static and/or dynamic obstacles. In our project, we
present an innovative approach for this path planning problem in
dynamic environments when the robot doesn’t have any prior
knowledge about the map. Obstacles, such as walls and objects
are sensed using a laser sensor mounted on the robot, and a new
concept named Time Warps is used in order to predict the future
positions of moving objects and to avoid collisions between the
robot and moving obstacles by choosing an efficient path based
on those predictions. The path is calculated based on harmonic
potential fields and optimized by rubber band model.
The proposed method was tested based on several conducted
simulation scenarios employing MobileSim simulator for the
Pioneer P3-DX robot. Implementation of the algorithm was done by
C/C++ and CUDA programming using NVIDIA GTX 480 graphics
processor unit (GPU) to perform the processes in real time and
be used for real applications.
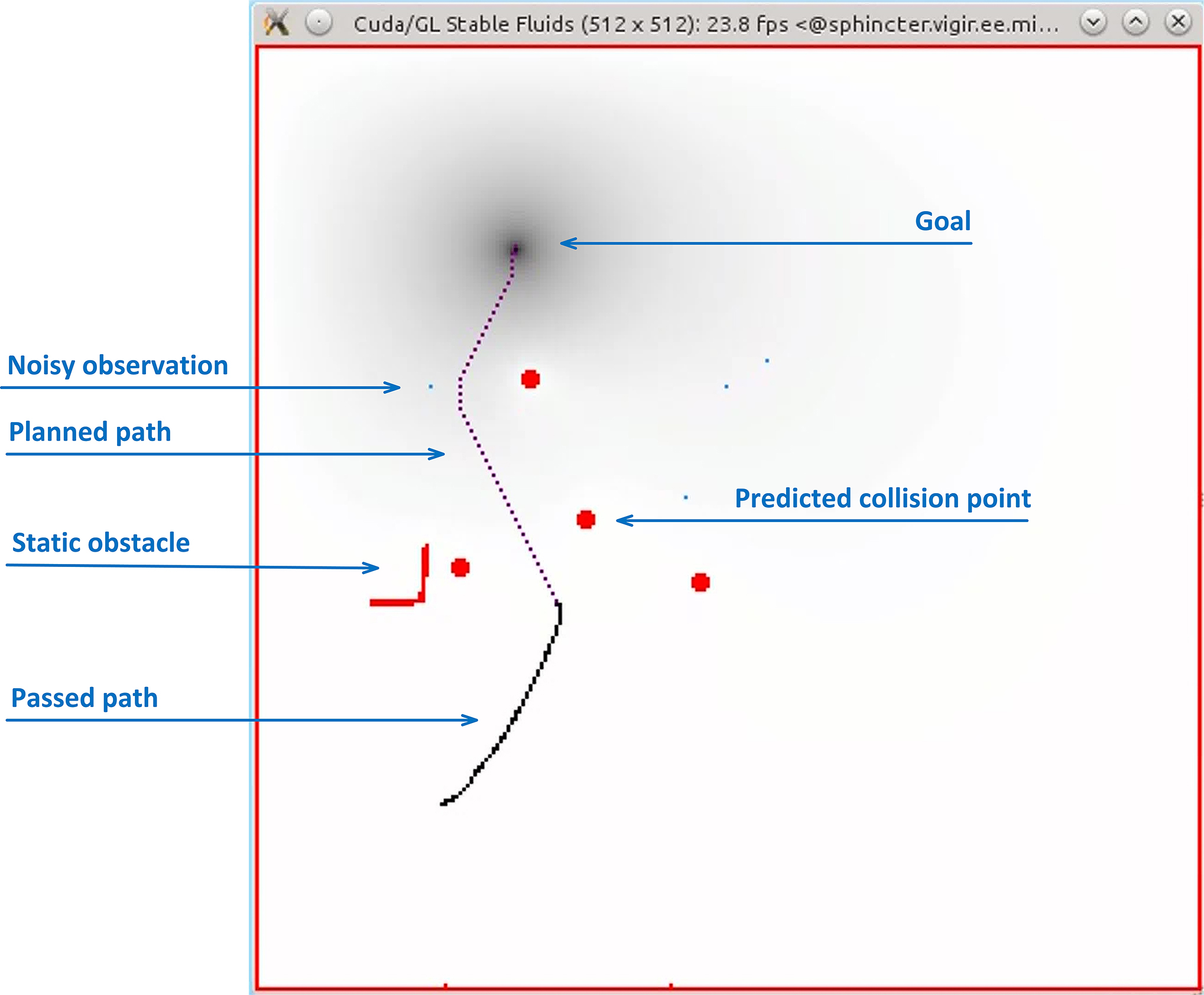
Demo Video
Previous work by
Ruizhi Hong
Path Planning using Harmonic Potentials on
the NVidia CUDA System(a)
CUDA
Implementation of a mobile robot path planner.
The algorithm is
based on harmonic potentials. The initial path is then optimized using an
elastic model that simulates smoothing forces. The parallel algorithm
is implemented on CUDA in order to run in real time.
As shown in the figure above,
the blue path is the output of the harmonic potential. The white pixels
represent high energy potentials while the black pixels represent lower
potentials. Red pixels are obstacles. The final and smooth path, in yellow, goes
from higher potentials (starting position) to lower potentials (goal position).
The parallel
version of the algorithms runs 10 times faster on CUDA than a typical CPU --
depending on the GPU and CPU platforms.
References
-
S. Farzan
and G. N. DeSouza, "Path Planning in Dynamic Environments
Using Time Warps". (Ready to be submitted)
-
Hong, R, and DeSouza, G. N.,
"
A Real-Time Path Planner for a Smart Wheelchair
Using Harmonic Potentials and a Rubber Band Model,",
in the Proceedings of the
2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotic System (IROS).
-
DeSouza G.N., Kak A.C.,
"
Vision for Mobile Robot Navigation",
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
Vol. 24, No. 2, pp. , Feb. 2002.
(a) This research made use of GTX480s and Tesla's S1070 donated by NVIDIA via their Academic Partnership Program.
|